Translation memory: What is it, how does it work and key benefits for a business
Picture this: you must update a user manual for a specific gadget. What’s your strategy? Do you rewrite it from scratch? Or do you prefer to amend only what’s necessary to make it current and relevant?
Now, let’s shift gears to the world of e-commerce. Imagine a business with this amazing pair of shoes, available in five colours. Will they type the same product description five times, one for each shade? Or will they find a smarter, more efficient way of doing this?
As you look for intelligent solutions when writing repetitive content in your native language, you must also explore the tools available to maximise efficiency in your translation process. This is where a Translation Memory (TM) comes in, transforming how companies manage multilingual content.
A TM is a fundamental component in the translation and localisation industry. It offers an innovative solution to ensure that every translation project builds upon the last and eliminates the need to retranslate your materials.
In this blog post, we will look into translation memory and how it works. We will share the best practices to leverage this technology, improve quality and consistency and save your business money.
What is a translation memory?
So, what exactly is translation memory? At its core, a TM is a database that stores “segments” (phrases, sentences, paragraph parts) previously translated, allowing translators to reuse them in future projects. But a translation memory is not just a database of text segments; it’s a living archive that grows with each project and becomes a source of accurate, reusable content.
Termbase vs translation memory
A termbase is essentially a glossary of pre-established terms and phrases specific to a company or industry. For example, a business may prefer to use the English words “email marketing” or “marketing automation” in other languages instead of the equivalent translation because the English terms are widely used, and they will provide these “instructions” in a termbase.
Why is a termbase different to a TM? While a termbase acts as a dictionary that translators follow to use the correct terminology, a translation memory retrieves words or sentences already translated that language professionals can reuse and adapt to fit a new text.
Machine and AI translation vs translation memory
Machine translation and AI translation usually come with the dilemma of how accurate and natural translations are; they combine different technologies, such as Neural Machine Translation and Machine Learning, to automatically translate text from one language to another without human involvement.
Unlike these automated solutions, professional translators build and continually refine a translation memory, providing a quality that machine translation systems struggle to match without sacrificing efficiency.
How does a translation memory work?
Modern computer-assisted translation (CAT) tools come with a translation memory as one of their features. This technology will scan the source text and compare it to the entries in the translation memory when a translator opens a document in a CAT tool. Then, the TM will recommend a translation for the new segment if there are matching or similar segments.

The translator can now view both the source text pulled from the translation memory and the suggested translation. They can accept, reject or modify the suggested translation before moving on to the next segment. This post is sponsored by our partners Wigs
As translators work on the new text, new segments are created in the translation memory, adding to the number of available segments ready to be used next time.
Types of translation memory matches
As mentioned above, a translation memory suggests a translation for a new segment if
there are matching or similar segments. A TM has a rating system for defining how close the translation matches are. This leads to different types of matches:
- Perfect or exact match: The source text segment is identical (100% match) to a segment in the translation memory.
- Context match: This is also a perfect match with the same preceding and subsequent sentences, which usually means that the text is used in the same context as the previously translated text and is more likely to be correct.
- Fuzzy match: The source text segment is similar but not identical (for example, 75% match) to a segment in the translation memory, requiring minor adjustments. The higher the percentage of the fuzzy match, the closer the match is.
5 best practices for TM management and use cases
Now that you know why it makes sense to use a translation memory, there are a few steps you can take to make sure you are making the most of it.
1) Using previous translations
If you have an existing translation memory – whether it is from a previous translation agency or your team members – you can import it into a new TM (just make sure that the quality of the translations is good before importing and using them in a new document).
You may also have translated some materials in the past but did not create a translation memory. In this case, aligning your translation memory by uploading the source and target files is possible. Once the alignment is complete, you can use the TM in your CAT tool as normal.
2) Creating project-specific translation memories and a master translation memory
Work with a language service provider who allows you to create a project-specific translation memory and a master translation memory. A project-specific translation memory and a master translation memory can both be used simultaneously. But, by maintaining your master translation memory in read-only mode, you can prevent incorrect translations from being added.
Project-specific translation memories are a good idea for any new project, particularly when multiple translators are working simultaneously, because it provides them with real-time segment matches to ensure consistency and avoids two people translating the same thing twice.
Once the translations of a project-specific translation memory have been reviewed and approved, they can be added to the master translation memory. By doing this, you will ensure that only accurate translations enter the master TM, preventing any potential errors.
3) Prioritising suggestions
In projects involving multiple translation memories, ranking them in order of reliability or adding penalties to their matches is common. This hierarchy ensures that the most trusted TMs provide the top suggestions, reflecting higher match scores.
Linguists can thus easily access and leverage the best translations right away. This prioritisation streamlines the translation process, ensuring that linguists first work with the highest quality and most relevant translation suggestions.
4) Updating and consolidating your TM
It is essential to update and consolidate your TM to keep it accurate and effective. As your project develops, you do not only need to add new translations but also review and refine existing segments to ensure they stay accurate.
Additionally, identifying and consolidating duplicate segments is crucial. Sometimes, multiple translations may exist for the same source text. In such cases, evaluating and retaining the most suitable translation while removing others will help you streamline your TM, making it more efficient and reducing inconsistency during translation tasks.
5) Evaluating how you will benefit from a translation memory
Using a translation memory is always a good idea as long as there is repetitive text. But be aware that there are some exceptions. For example, if you translate a new marketing campaign with catchy slogans and tag lines, the matches or repetitions from previous marketing materials are likely limited. Therefore, you do not need to use a TM; if your translators use it, do not expect it to be as effective as with other types of texts.
But most times, you will undoubtedly benefit from using a translation memory. Let’s look at different types of content to understand better how useful a TM can be.
Technical documents and manuals
Operating and maintenance manuals with repetitive text are good examples of content that can benefit most from a translation memory. When a company introduces a new model, much of the manual from previous versions can be reused, as typically, only a few features change or are added. This scenario is ideal for a TM, and you can expect a lot of perfect and fuzzy matches, streamlining the translation process.
Product descriptions and e-commerce content
A translation memory can be highly beneficial in e-commerce, particularly for product descriptions on platforms like Amazon. Consider a brand selling coffee in two forms: as beans and ground. Product details, like description, origin, and taste, remain identical for both forms.
A TM enables translators to focus only on the differences (beans or ground) while efficiently reusing the identical segments for the rest of the description. This application of a TM not only saves time but also maintains consistency across product listings.
Software and website localisation
A TM significantly enhances the translation process when translating or localising software or a website. UI elements like menu names and button labels must remain consistent across current and future versions. Once an element is translated and stored in the TM, it can be reused, ensuring consistency in user experience and making the software or website easier to use.
Key benefits of a translation memory for a business
Using a translation memory means linguists avoid re-translating the same content. The TM grows as more content is translated, which benefits businesses and language service providers in terms of quality, cost savings, and time efficiency.
Quality improvement and consistency
Maintaining consistency can be challenging for translators, especially when projects are large, spaced over time, or multiple translators are working on a text simultaneously. By allowing language professionals to reuse approved translations, a TM eliminates the need for time-consuming and unreliable research into past translations.
In a challenging English-to-Italian project involving 145,647 words, Ampere Translations had a tight deadline of 7 days. Multiple linguists worked simultaneously on the document to complete this project on time without a pre-established term base. The TM played a crucial role in this scenario. It provided real-time matches and results to each linguist, ensuring consistency throughout the document and allowing for the project’s timely completion.
Inconsistent translations can negatively impact end-user experience, resulting in negative customer feedback and possible brand damage. Thus, employing a TM ensures translation consistency and quality for the benefit of all parties.
Faster turnaround times
According to most language experts, a translation memory facilitates faster translation delivery. For time-sensitive projects like product launches, faster translation enables businesses to quickly communicate in multiple languages to meet the demands of their global customers.
Faster turnaround times also mean that companies can seize market opportunities. For example, quickly translating a trending article or hot-selling product description can attract more customers.
Lower cost
Over time, a translation memory helps reduce costs. Because there is less work for translators to do when a TM is provided, language service providers frequently offer discounted rates for exact and fuzzy matches. Thus, repetitive content projects can save a significant amount of money.
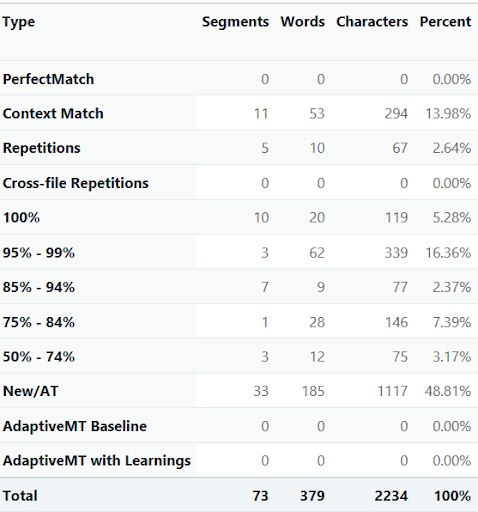
For example, Ampere Translations completed an English-to-German translation project involving 54,239 words. The client wanted to maintain consistency with previously translated material and potentially save money. By importing this material into the translation memory, we achieved 32% high fuzzy matches (from 85% to 101% matches). This example underscores the practical efficiency and consistency benefits of using a TM.
Nevertheless, it is worth noting that setting up and maintaining a TM involves an initial investment – in particular in projects like the one from the example above, where alignment from previously translated documents was required – so the cost should always be balanced against the potential benefits.
Embracing the future with translation memory
A translation memory is much more than a database; it’s a valuable tool that grows and evolves with your business, ensuring that each translation builds on the previous one for increased quality and consistency and the potential for reduced costs.
As we embrace the new era of AI and technology-driven translation solutions, a TM is an investment in your business’s efficiency and global reach, ensuring that you stay ahead in a world where communication and accuracy are key.
Are you ready to streamline your translation process and take your business’s global communication to the next level? Contact Ampere Translations today to harness the full potential of translation memory and drive your business forward.
